Laser cutting techniques use lasers to slice material. This technique is very fond of hobbyists and is also widely used in industrial use. In this blog we will learn what is Laser cutting and its different types.

Laser Cutting: The rapid growth of technology and computers led to many new inventions in the manufacturing sector.
One of those remarkable achievements is the CNC Machining process.
It has helped industries to develop high-precision metal parts for engineering development.
In this article, we will discuss the basics of Laser Cutting which is again one of the types of CNC machining.
The laser cutting process is used not only for cutting metal sheets but also for other materials like clothes, rubber, etc.
There are many benefits of using the LASER beam for cutting metal. We will discuss them later in this article.
Overall, it is a very popular manufacturing process; understanding it will help you a lot.
You may be interested in our blog mentioned below about object manufacturing.
• Types of 3D Printers: Complete Guide – SLA, DMLS, FDM, SLS
• What Is 3D Printing? Types OF 3D Printing.
But before we start discussing how a laser beam is used to cut the metals, let us first understand “What Is LASER?”
What is LASER?
Laser stands for Light Amplification Using Stimulated Emission of Radiation.
Using this LASER technology, we can produce a narrow beam of light that can be used for various purposes.
Do not think of LASER as a usual light source because generic light sources produce light with many different wavelengths.
Let me explain,
Light is a wave.
Each wave has a wavelength. Also, different colours have different wavelengths.
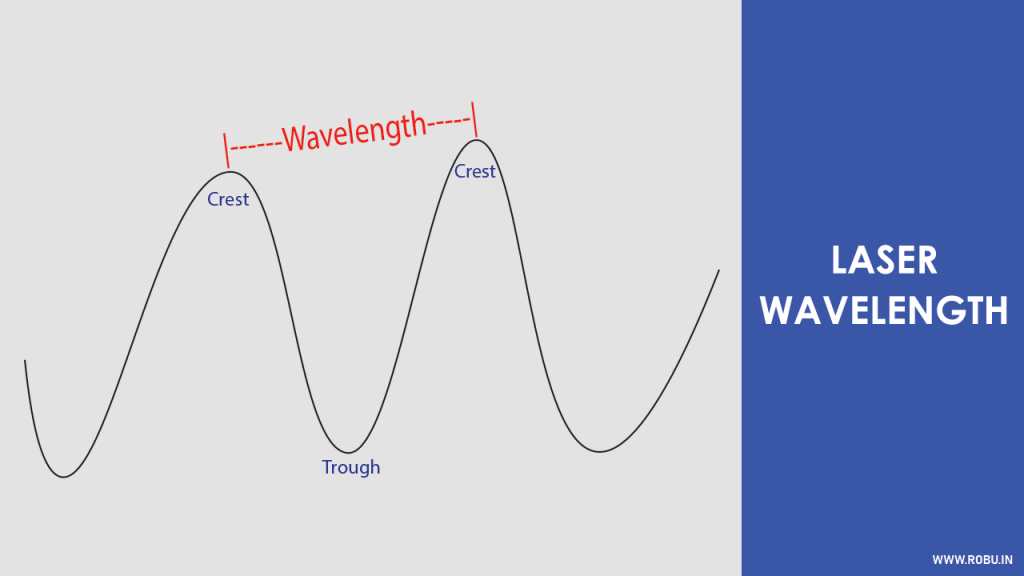
Generic Light Sources
Light from generic (bulb & flashlight) sources consists of different colours.
That means such a light source consists of different waves.
Due to these different waves, the light from a bulb or flashlight seems to spread and scattered in different directions.

LASER as A light source
Unlike generic sources, a LASER comprises a single colour, i.e., Red, Blue, Green.
Such light of single colour consists of only one wave [so does the wavelength].
LASER beam is made intense and narrow by packing several waves of a single colour travelling in one particular direction.
Now, in the following section, we will learn how this intense source of light [LASER] is used for cutting the materials,

How Does LASER Cutting Work?
Laser cutting is nothing but the focusing of the kilo-watts of electrical energy onto a single spot.
This high-energy can heat, melt and partially vaporize the material it strikes.
In laser cutting, CNS is used to direct a high-power LASER beam to cut the metals (other materials).
Let’s start with the basics,
Generally, a resonator is used to create a high-power laser beam.
There are various types of laser generator,
- CO2 Laser
- Neodymium Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet (Nd:YAG) Laser
- Fibre Lasers
Step #1 – Generating the Laser Beam
CO2 lasers are very popular because of their affordable price and accuracy.
It can cut non-metallic materials as well as thin sheets of aluminium and non-ferrous metals.
It produces laser by passing electricity through a tube that contains a mixture of Carbon Dioxide, Nitrogen, Hydrogen, and Helium gas. The mirror is placed at each end of the tube: one of which is fully reflective and the other is partial.
The wavelength of the generated light [laser] by CO2 laser is in the infrared region, so it can’t be seen through the human eyes.
Step #2 – Focusing (Narrowing) the Laser Beam
This laser is then passed through a couple of specially designed mirrors before striking the material.
The purpose of this mirror is to make the laser beam more intense and narrow.
E.g., A laser resonator produces rays of coherent light with a diameter of 1.5 to 2 mm. This laser beam is intensified to the diameter of 0.025 mm by passing it through the mirror.
So, a laser beam isn’t focused directly onto the material. But it is narrowed to a certain extent before it passes through the nozzle and strikes the material.
These mirrors work very identical to a magnifying glass that focuses sun rays and burns the paper.
We can control laser beam intensity, length, and heat output depending upon the metal we wish to cut.
Step #3 – Cutting the Material
Before starting to cut the material, a pierce (kerf) is formed by this high-intensity laser beam at the edge of the material.
Sidenote: Kerf is referred to the amount of material the laser takes away while cutting or the width of the groove formed while cutting.
A capacitive height control system is used to maintain the distance between the nozzle and the material.
Once the kerf is formed, the laser beam then follows the G-code to trace the material under design.
G-code is the set of digital instructions given to the CNC machine (Laser Cutting Machine) by computers.
Unlike the old days where engineers had to write the G-Code manually, nowadays, few software are capable of converting the 3D model into G-code.
Alternatives to Laser Cutting
Despite the popularity and advantages offered by Laser cutting, there are few limitations as well,
- High electricity consumptions
- Can’t cut thick materials
- The time required for cutting material depends upon the type of material
- And more
Due to the above drawbacks, people try to find out alternatives to laser cutting.
Let them discuss this shortly.
1 Milling

Milling is the oldest and most common machining process used in manufacturing.
This process uses multi-sharp tools, also known as milling cutters, to remove unwanted materials.
Milling cutters are made up of multiple cutting points that rotate and trims excessive material from the workpiece.
Rotary milling cutters are mounted on a spindle to rotate it.
In this process, a workpiece is secured using a fixture (a part of the milling machine). Using CNC, the milling cutter is advanced towards this workpiece with maximum precision and accuracy.
Milling is used to making holes, pockets, slots, and contours of the symmetric shape.
Disadvantages of Milling Process
- It requires skilled workers to operate accurately
- Cutting radial cuts is not possible
- Risk of temperature and thermal stress
2 Wire EDM

Wire EDM stands for Wire Electric Discharge machining.
The Wire EDM uses a very thin single-strand metal wire to cut the workpiece by the heat from an electrical spark.
This process is also known as spark machining.
In this process, the wire strand doesn’t directly touch the workpiece. The metal wire is constantly charged to the desired voltage. This wire is surrounded by de-ionized water, which acts as a dielectric medium.
When the voltage reaches the desired value, a spark is generated between the metal wire and respective workpiece area, which then melt down the small portion of the workpiece.
The Wire EDM process is used for the small workpiece and designing complex shapes that require an excellent surface finish.
Disadvantages of Wire EDM
- The process of cutting is prolonged
- Cannot cut non-conductive materials
- Risk of temperature and thermal stress
3 Punch Press

Punch Press is used for cutting the sheet of metals by applying the pressure.
Generally, it consists of a punch and a die. The workpiece is placed between these two parts.
Punch is advanced onto the workpiece, which then goes through the forming, bending, and drawing.
Punch Press is operated by electric motors, the rotational energy of motors is converted into reciprocating ram. This reciprocating ram of the machine drives the punch and creates very high pressure on the workpiece.
Disadvantages of Punch Press
- Produces very loud noise
- Requires experts to install and maintain
- Not suitable for small-scale production
- Risk of temperature and thermal stress
4 Water Jet

Water Jet is another excellent invention in the manufacturing industry.
It creates a high-pressure jet capable of cutting nearly all types of materials using water and abrasive.
The jet of water creates an extremely high pressure of 6000 bar, which equals the 1000 m/s.
A costly (sintered boride or tungsten carbide) nozzle is used to convert the water from a high-pressure pump into a high speed, high density, and ultra-high pressure water jet.
It has been used in the mining and aerospace industry for a very long time.
The final design cut using a water jet has a highly smooth finish.
Disadvantages of Water Jet
- It has a very high running cost
- It consumes lots of abrasive which is expensive
Advantages of LASER Cutting
LASER Cutting offers various benefits over other cutting processes used in the industry.
Here is the list,
- High precision and accuracy
- Speed of cutting is comparatively high
- Cleaning (smoothing) of the final product is not required
- Running cost is low
- No risk of temperature and thermal stress
- It is a non-contact type cutting (there is no physical contact between laser cutter and workpiece)
- Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) is tiny
- No damage and wrapping of the workpiece
- Safer than other similar cutting processes
- Can work with various materials like metal sheets, wood, paper, plastic, acrylic, diamonds, glass, etc.
- Laser cutting is also found in the medical and food industries
Material Suitable for Laser Cutting
Let’s discuss what type of materials a laser cutter can cut.
A laser cutter is capable of cutting a wide variety of materials that includes both metals and non-metals.
#1 – Metals
- Mild Steel
- Aluminium
- Stainless Steel
- Non-ferrous metals
#2 – Non-Metals
- Wood
- Paper
- Glass
- Acrylic
- Diamonds
- PMMA (Poly Methyl Methacrylate)
- POM (Polyoxymethylene)
Materials NOT Suitable for Laser Cutting
Here is the list of materials that we cannot cut using LASER Cutting,
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
- Fibre Glass
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
- Polycarbonate
- Polypropylene Foam
- Polystyrene Foam
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
- Coated Carbon Fiber





Can we cut Polystyrene paper of 5mil or 0.127mm thickness using laser? Its melting point is 260degrees.
No, it is not possible to cut Polystyrene paper with laser. You can use Professional Foam Cutter to cut the paper
Excellent information shared. Request you to please it with more latest upgrades and updates available time to time with more details.